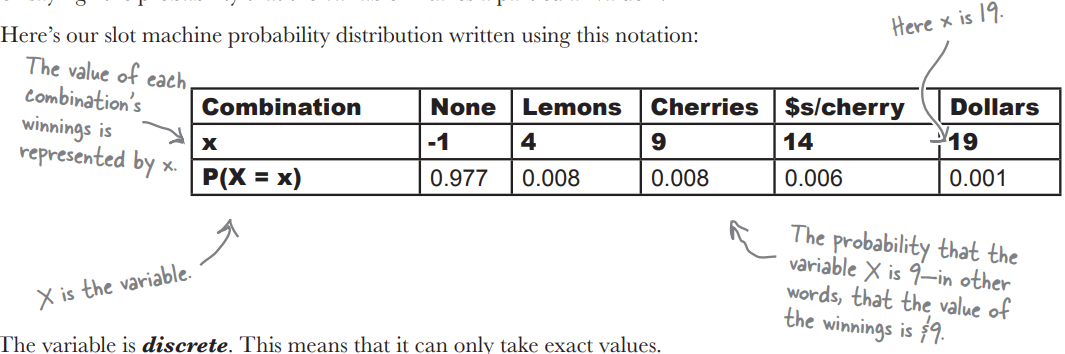
Discrete Probability Distributions
Discrete Probability Distribution
a type of probability distribution that shows all possible values of a discrete random variable along with the associated probabilities
Example:
Expectation
Variance
Standard Deviation
Independent Observation
If you have independent variables
Linear Transforms
If you have a variable
If you have a variable
Sources: 1